In today’s article, we will show you how to automate Ansible security scanning using KICS within GitHub Actions by leveraging a self-hosted runner. This setup ensures that every code push or pull request triggers a scan of Ansible playbooks, detecting vulnerabilities before merging or deployment.
Why This Automation required for Ansible Security Scanning
DevOps teams routinely enforce code linting and style checks, but they often overlook automating security scans for infrastructure as code. By integrating KICS, an open‑source tool for detecting misconfigurations, you can inject security into your CI/CD flow. Moreover, using a self‑hosted runner gives you full control over dependencies, environment configuration, and execution.
The Workflow Overview
Below is a step‑by‑step breakdown of the automated process:
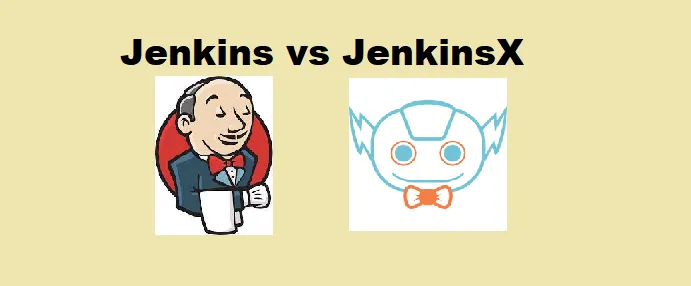
- Developer pushes Ansible
.ymlfiles to GitHub or opens a pull request. - GitHub Actions triggers the workflow.
- Self‑hosted runner (configured with KICS) executes the job.
- The workflow checks out code and identifies changed YAML files.
- KICS scans the modified files for Ansible‑specific vulnerabilities.
- The pipeline generates the resulting HTML report and uploads it as an artifact.
This efficient flow automatically scans every change to Ansible playbooks, helping developers catch security issues before merging.
Setting Up the Self‑Hosted Runner with KICS
On the self-hosted runner host, the system performs the following steps:
# Clone KICS source code
git clone https://github.com/Checkmarx/kics.git
cd kics/
# Vendor modules
go mod vendor
# Download and install Go 1.22.3
curl -LO https://go.dev/dl/go1.22.3.linux-amd64.tar.gz
sudo tar -C /usr/local -xzf go1.22.3.linux-amd64.tar.gz
# Add Go to PATH
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/go/bin
export GOROOT=/usr/local/go
# Confirm Go installation
go version
# Install make for building KICS
sudo yum install make -y
go mod vendor
make build
# Add KICS to PATH
export PATH=$PATH:/home/nikhil/kics/bin/
# Link query assets required by KICS
ln -s /root/kics/assets/ ./assetsAfter this setup, the runner is fully capable of executing the kics CLI to scan Ansible playbooks.
CI/CD: The GitHub Actions Workflow
Below is the workflow YAML file. Notice how it focuses on detecting and scanning only the changed YAML files:
name: Ansible Security Scan with KICS
on:
push:
pull_request:
branches:
- '*'
jobs:
kics-scan:
runs-on:
- self-hosted
steps:
- name: Checkout Code
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Get Changed YAML Files
id: changed-yaml
run: |
CHANGED_FILES=$(git diff --diff-filter=AM --name-only ${{ github.event.before }} ${{ github.sha }})
YAML_FILES=""
for file in $CHANGED_FILES; do
if [[ $file == *.yml || $file == *.yaml ]]; then
YAML_FILES="$YAML_FILES $file"
fi
done
echo "yaml-files=$YAML_FILES" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
- name: Add KICS to PATH & Resouces path
run: |
echo "/home/nikhil/kics/bin" >> $GITHUB_PATH
cp -r /home/nikhil/kics/assets ./assets
- name: Run KICS Scan and Generate HTML Report
if: ${{ steps.changed-yaml.outputs.yaml-files != '' }}
run: |
mkdir -p kics-results
echo "Scanning: ${{ steps.changed-yaml.outputs.yaml-files }}"
kics scan -p ${{ steps.changed-yaml.outputs.yaml-files }} --type ansible --report-formats html --output-path kics-results || true
- name: Upload KICS HTML Report
if: ${{ steps.changed-yaml.outputs.yaml-files != '' }}
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
with:
name: kics-html-report
path: kics-results/results.htmlEach step is clearly labeled to illustrate the flow of Ansible security scanning using KICS and GitHub Actions.
Demo: Scan with and without Vulnerabilities
We used two sample playbooks to demonstrate how KICS detects misconfigurations in Ansible.
test-playbook.yml(No Vulnerabilities)
- name: Test PB
hosts: localhost
tasks:
- name: Test task
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "testing github action workflow using kics"KICS Report Output:
The HTML report shows 0 vulnerabilities. The scan ran successfully and showed a green status, confirming that it found no security issues in the playbook.

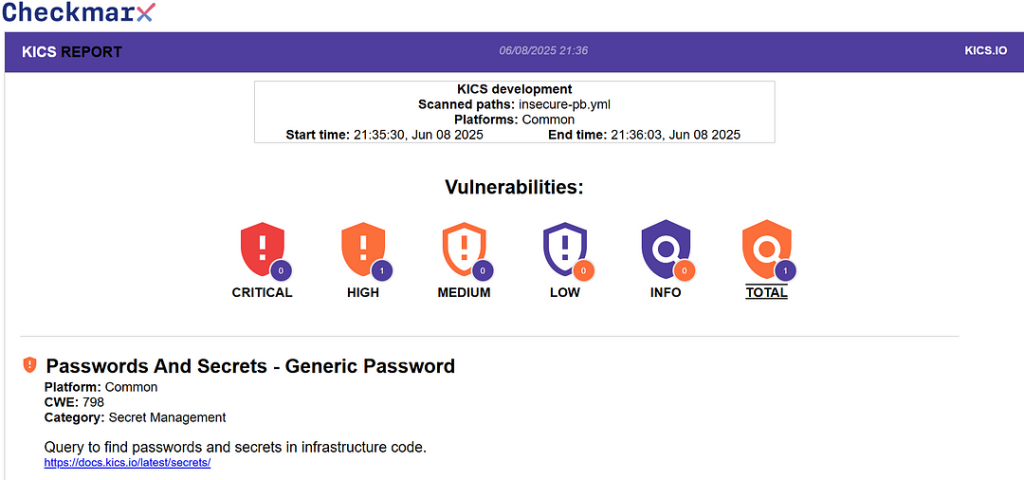
- insecure-pb.yml (With Vulnerability)
- name: insecure
hosts: all
tasks:
- name: run shell
shell: apt-get install -y nginx
- name: weak password
user:
name: user12
password: "password"KICS Report Output:
The HTML report flags 1 High-severity vulnerability:
- Query Name: Password In Clear Text
- Severity: High
- Description: Detected usage of a cleartext password inside an Ansible playbook.
This serves as a great example of how KICS can catch potentially risky code before it reaches production.
Conclusion
To summarize:
- A self‑hosted GitHub Actions runner was configured with Go and KICS.
- A precise workflow was created to automate Ansible security scanning.
- HTML vulnerability reports are produced and archived with each scan.
- You can check for insecure playbooks on every change, improving your DevSecOps posture.
🔗 For further guidance, checkout other blogs: